Nitric acid
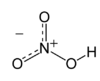

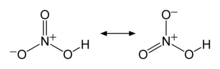

Nitric acid (HNO3), also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxicstrong acid.
Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% Nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming Nitric acid. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming Nitric acid is further characterized as white fuming nitric acid or red fuming nitric acid, at concentrations above 95%. At room temperature, Nitric acid tends to rapidly develop a yellow color due to decomposition. Nitric acid is also commonly used as a strong oxidizing agent.
Properties
Pure anhydrous Nitric acid (100%) is a colorless mobile liquid with a density of 1.512 g/cm3 which solidifies at −42 °C to form white crystals and boils at 83 °C. When boiling in light, and slowly even at room temperature, there is a partial decomposition with the formation of nitrogen dioxide following the reaction:
4 HNO3 → 2 H2O + 4 NO2 + O2 Thus, anhydrous Nitric acid should be stored below 0 °C to avoid decomposition. The nitrogen dioxide (NO2) remains dissolved in the Nitric acid coloring it yellow, or red at higher temperatures. While the pure acid tends to give off white fumes when exposed to air, acid with dissolved nitrogen dioxide gives off reddish-brown vapors, leading to the common name "red fuming acid" or "fuming Nitric acid". Fuming Nitric acid is also referred to as 16 molar Nitric acid. It is the most concentrated form of Nitric acid at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP).Nitric acid is miscible with water and distillation gives a maximum-boiling azeotrope with a concentration of 68% HNO3 and a boiling temperature of 120.5 °C at 1 atm, which is the ordinary concentrated Nitric acid of commerce. Two solid hydrates are known; the monohydrate (HNO3·H2O) and the trihydrate (HNO3·3H2O).Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are soluble in Nitric acid and this property influences more or less all the physical characteristics depending on the concentration of the oxides. These mainly include the vapor pressure above the liquid and the boiling temperature, as well as the color mentioned above.Nitric acid is subject to thermal or light decomposition with increasing concentration and this may give rise to some non-negligible variations in the vapor pressure above the liquid because the nitrogen oxides produced dissolve partly or completely in the acid.
ليست هناك تعليقات:
إرسال تعليق